Introduction
Swing trading is a popular trading strategy that aims to capture short to medium-term price movements in financial markets. Unlike day trading, which involves opening and closing positions within the same trading day, swing trading typically involves holding positions for several days to weeks. This article provides a comprehensive guide to swing trading, covering key principles, technical analysis tools, profitable setups, entry and exit strategies, risk management techniques, common mistakes to avoid, and additional resources for successful swing trading.
What is Swing Trading?
Swing trading is a trading style that focuses on capturing “swings” or fluctuations in asset prices over relatively short timeframes. The goal of swing trading is to profit from the cyclical nature of price movements, buying low at support levels and selling high at resistance levels. Swing traders often use technical analysis to identify potential entry and exit points based on price patterns, trends, and indicators.
Key Principles and Concepts of Swing Trading
Several key principles and concepts underpin successful swing trading:
Key Principles and Concepts of Swing Trading
Successful swing trading relies on several key principles and concepts that guide traders in identifying profitable opportunities and making informed trading decisions. Understanding these fundamental principles is essential for mastering the art of swing trading. Here are the key principles and concepts of swing trading explained in detail:
- Trend Analysis:
Trend analysis is a fundamental principle of swing trading, where traders aim to identify and capitalize on the prevailing direction of price movement. Swing traders often follow the trend of the market or the underlying asset, seeking to align their trades with the primary trend. By recognizing whether the market is in an uptrend, downtrend, or range-bound phase, swing traders can better determine the most favorable trading opportunities.
In an uptrend, swing traders focus on buying opportunities, aiming to enter trades when prices are rising and pullbacks occur within the context of the upward trend. Conversely, in a downtrend, swing traders look for selling opportunities, seeking to enter trades as prices decline and retracements occur within the downtrend. Trend analysis helps swing traders filter out noise and focus on trading in the direction of the prevailing trend, increasing the probability of successful trades.
- Support and Resistance:
Support and resistance levels are critical concepts in swing trading that help traders identify key price levels where buying and selling interest is concentrated. Support levels represent price zones where buying pressure is expected to emerge, preventing prices from falling further. These levels often coincide with previous lows or significant price points where buyers have historically entered the market, creating a barrier to further downside movement.
Resistance levels, on the other hand, represent price zones where selling pressure tends to outweigh buying pressure, limiting upward price movements. These levels typically coincide with previous highs or significant price points where sellers have historically entered the market, creating a barrier to further upside movement.
In swing trading, traders pay close attention to support and resistance levels as they provide valuable insights into potential entry and exit points. Breakouts above resistance levels or bounces off support levels can signal potential trading opportunities, while breaches of these levels may indicate trend reversals or continuation patterns.
- Price Patterns:
Price patterns are recognizable formations that occur on price charts and provide valuable insights into market sentiment and potential price reversals. Swing traders actively look for specific price patterns, such as chart patterns and candlestick patterns, to identify potential trade setups with favorable risk-to-reward ratios.
Chart patterns, such as head and shoulders, double tops, double bottoms, triangles, and flags, are visual representations of price movements that indicate potential trend reversals or continuation patterns. These patterns are formed as a result of shifting supply and demand dynamics in the market and can provide valuable clues about future price movements.
Candlestick patterns, such as doji, hammer, engulfing patterns, and evening stars, are formed by the open, high, low, and close prices of a specific time period. These patterns often signal changes in market sentiment and can help traders anticipate potential price reversals or continuations.
By recognizing and interpreting price patterns, swing traders can gain a deeper understanding of market dynamics and make more informed trading decisions. Price patterns serve as powerful tools for identifying entry and exit points, managing risk, and maximizing trading profits in swing trading.
In conclusion, understanding the key principles and concepts of swing trading is essential for traders looking to succeed in the dynamic and fast-paced world of financial markets. By mastering trend analysis, support and resistance levels, and price patterns, swing traders can enhance their trading skills, increase their profitability, and achieve long-term success in the markets.
Technical Analysis Tools for Swing Trading
Swing traders rely on various technical analysis tools to identify trading opportunities and make informed decisions. Some commonly used tools include:
- Moving Averages: Moving averages help traders identify trends and potential trend reversals by smoothing out price fluctuations over a specified period. The crossover of different moving averages (e.g., the 50-day and 200-day moving averages) can signal changes in trend direction.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. It oscillates between 0 and 100 and is used to identify overbought and oversold conditions in the market, indicating potential reversal points.
- Fibonacci Retracement Levels: Fibonacci retracement levels are horizontal lines drawn on a price chart to identify potential support and resistance levels based on key Fibonacci ratios (e.g., 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%). These levels are often used by swing traders to anticipate price reversals or continuation patterns.
Identifying Profitable Swing Trading Setups
Successful swing traders focus on identifying high-probability trading setups that offer favorable risk-to-reward ratios. Some common swing trading setups include:
Identifying Profitable Swing Trading Setups
Successful swing trading relies on the ability to identify high-probability trading setups that offer favorable risk-to-reward ratios. By focusing on setups that align with the prevailing market conditions and offer clear entry and exit signals, swing traders can increase their chances of success. Here are two common swing trading setups that traders often look for:
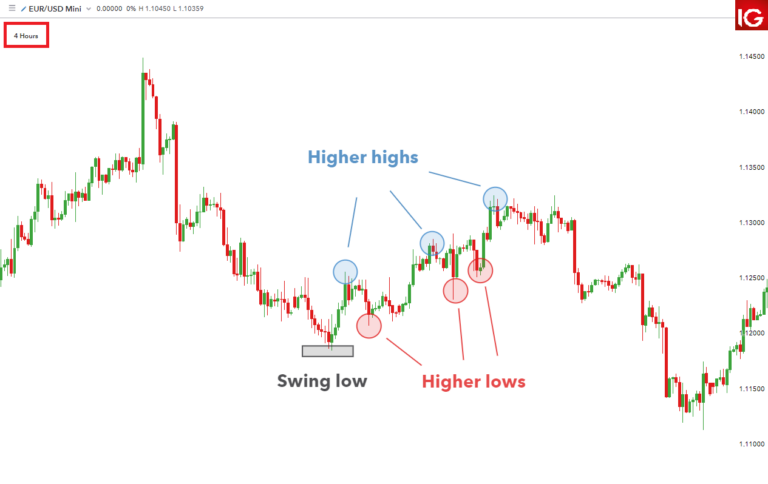
- Trend Continuation Trades:
Trend continuation trades are setups that occur within the context of an existing trend, offering an opportunity to enter the market in the direction of the prevailing trend. These setups typically occur when the price retraces or pulls back temporarily against the trend before resuming its upward or downward movement. Swing traders aim to enter trades during these retracements at more favorable prices, allowing them to ride the trend for potential profits.
To identify trend continuation trades, swing traders look for the following characteristics:
- A well-defined trend: Before considering a trend continuation trade, swing traders ensure that there is a clear and established trend in place, either upward (bullish) or downward (bearish).
- Retracement or pullback: During an uptrend, swing traders look for temporary pullbacks or retracements in price, which provide an opportunity to enter long positions at a lower price. Similarly, during a downtrend, swing traders look for short-term bounces or retracements, which allow them to enter short positions at a higher price.
- Confirmation signals: Swing traders wait for confirmation signals that indicate the resumption of the trend after the retracement. This may include bullish reversal patterns (e.g., bullish engulfing, hammer) in an uptrend or bearish reversal patterns (e.g., bearish engulfing, shooting star) in a downtrend.
- Risk management: To manage risk, swing traders place stop-loss orders below (in an uptrend) or above (in a downtrend) the recent swing low or high, respectively. This helps protect against adverse price movements that could invalidate the trade setup.
Overall, trend continuation trades allow swing traders to capitalize on the momentum of the prevailing trend while managing risk effectively.
- Trend Reversal Trades:
Trend reversal trades are setups that occur when the price reaches a key support or resistance level and shows signs of a potential reversal in the prevailing trend. These setups often occur after an extended trend and can signal a shift in market sentiment and direction. Swing traders look for confirmation signals, such as bullish or bearish candlestick patterns, to enter trades in anticipation of a reversal.
To identify trend reversal trades, swing traders look for the following signs:
- Confluence of factors: Swing traders look for key support or resistance levels that align with other technical indicators or price patterns, increasing the likelihood of a reversal. These levels may include Fibonacci retracement levels, trendlines, or previous swing highs/lows.
- Reversal patterns: Swing traders wait for confirmation signals, such as bullish reversal patterns (e.g., hammer, morning star) at key support levels in a downtrend or bearish reversal patterns (e.g., shooting star, evening star) at key resistance levels in an uptrend.
- Volume confirmation: Swing traders often look for an increase in trading volume accompanying the reversal signal, indicating strong market participation and confirming the validity of the setup.
- Risk management: As with trend continuation trades, swing traders implement risk management techniques by placing stop-loss orders above (in a downtrend) or below (in an uptrend) the recent swing high or low, respectively.
By focusing on trend continuation and reversal trades that offer favorable risk-to-reward ratios and clear entry and exit signals, swing traders can improve their trading performance and achieve consistent profitability in the markets.
Entry and Exit Strategies for Swing Trading
Entry and exit strategies are crucial components of a swing trader’s trading plan. While there are various approaches to entering and exiting trades, some common strategies include:
Entry and Exit Strategies for Swing Trading
Entry and exit strategies play a crucial role in the success of swing trading, as they determine the timing of trades and help traders maximize profits while managing risk effectively. While there are various approaches to entering and exiting trades in swing trading, some common strategies have proven to be effective for traders. Here are three key entry and exit strategies used in swing trading:
- Breakout Trading:
Breakout trading is a popular strategy among swing traders, which involves entering trades when the price breaks above resistance levels or below support levels. Breakouts often signify the potential continuation of an existing trend or the start of a new trend, presenting traders with profitable trading opportunities.
To execute breakout trades effectively, swing traders look for the following characteristics:
- Consolidation phase: Breakout trades typically occur after a period of consolidation or sideways movement, during which the price trades within a narrow range. This consolidation phase indicates a temporary pause in the trend, with potential energy building up for a breakout.
- Breakout confirmation: Swing traders wait for the price to break decisively above resistance levels (in an uptrend) or below support levels (in a downtrend), accompanied by strong volume and momentum. Breakout confirmation validates the trade setup and increases the likelihood of a successful trade.
- Entry and stop-loss placement: Swing traders enter breakout trades as soon as the breakout occurs, ideally at or slightly above (in an uptrend) or below (in a downtrend) the breakout level. Stop-loss orders are placed below (in an uptrend) or above (in a downtrend) the breakout level to limit potential losses if the breakout fails.
- Profit-taking: Swing traders aim to capture the momentum generated by the breakout by holding the position until the price shows signs of exhaustion or reaches a predetermined target level. Profit-taking strategies may involve scaling out of positions gradually or using trailing stop-loss orders to lock in profits as the trend progresses.
- Pullback Trading:
Pullback trading is another common strategy used by swing traders, which involves entering the market after a retracement within the context of an existing trend. Pullbacks occur when the price temporarily reverses against the prevailing trend before resuming its original direction, providing traders with opportunities to enter trades at more favorable prices.
To execute pullback trades effectively, swing traders look for the following characteristics:
- Established trend: Pullback trades are taken within the context of an established trend, either upward (in an uptrend) or downward (in a downtrend). The presence of a clear and well-defined trend increases the probability of a successful pullback trade.
- Retracement levels: Swing traders identify key support or resistance levels within the trend where price retracements are likely to occur. These levels may coincide with Fibonacci retracement levels, moving averages, trendlines, or previous swing highs/lows.
- Reversal signals: Swing traders wait for confirmation signals, such as bullish reversal patterns (in an uptrend) or bearish reversal patterns (in a downtrend), to indicate the end of the retracement and the resumption of the trend. These signals help validate the pullback trade setup and provide entry opportunities.
- Entry and stop-loss placement: Swing traders enter pullback trades as the price approaches key support or resistance levels within the trend, ideally at or near confluence zones where multiple technical factors align. Stop-loss orders are placed below (in an uptrend) or above (in a downtrend) the support or resistance level to limit potential losses if the pullback extends beyond expectations.
- Profit-taking: Swing traders aim to capture profits as the price resumes its original trend direction following the pullback. Profit-taking strategies may involve setting profit targets based on key support or resistance levels, Fibonacci extensions, or trend continuation patterns.
- Trailing Stop-Loss Orders:
Trailing stop-loss orders are a risk management technique used by swing traders to protect profits and minimize losses while allowing for potential upside gains. Trailing stop-loss orders automatically adjust the stop-loss level as the price moves in the trader’s favor, locking in profits and trailing behind the price to protect against adverse price movements.
To use trailing stop-loss orders effectively in swing trading, traders follow these steps:
- Initial stop-loss placement: Swing traders initially place a stop-loss order at a predetermined level based on their risk tolerance, the size of the trading account, and the volatility of the asset being traded. The initial stop-loss level is typically placed below (in an uptrend) or above (in a downtrend) the entry price.
- Trailing stop mechanism: As the price moves in the trader’s favor, the trailing stop-loss order adjusts automatically, trailing behind the price at a fixed distance or based on predefined criteria (e.g., percentage, volatility-based). The trailing stop follows the price at a specified distance, allowing profits to accumulate while protecting against sudden reversals.
- Protecting profits: Trailing stop-loss orders help swing traders protect profits by securing gains as the price moves in their favor. If the price reverses and triggers the trailing stop-loss order, the trade is closed automatically, locking in profits and preventing further losses.
- Managing risk: Trailing stop-loss orders also help swing traders manage risk by limiting potential losses if the trade moves against them. By continuously adjusting the stop-loss level in the direction of the trend, traders can protect capital and minimize drawdowns while allowing for potential upside gains.
Overall, entry and exit strategies are crucial components of a swing trader’s trading plan, allowing traders to enter trades at optimal price levels, manage risk effectively, and maximize profits. Whether utilizing breakout trading, pullback trading, or trailing stop-loss orders, swing traders aim to capitalize on favorable market conditions and exploit profitable trading opportunities in the dynamic world of financial markets.
Risk Management and Position Sizing in Swing Trading
Effective risk management is essential for preserving capital and ensuring long-term success in swing trading. Some key principles of risk management in swing trading include:
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders: Swing traders should always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on each trade. Stop-loss levels should be based on the trader’s risk tolerance and the volatility of the asset being traded.
- Position Sizing: Proper position sizing helps traders manage risk by determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each trade. Position sizes should be adjusted based on the size of the trading account, the risk per trade, and the distance to the stop-loss level.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Swing traders should aim for favorable risk-to-reward ratios on each trade, seeking opportunities where the potential reward outweighs the risk. A commonly used ratio is 2:1, meaning the potential reward is twice the size of the potential risk.
Best Swing Trading Strategies
Several swing trading strategies have proven to be effective for traders:
- Trend Following: This strategy involves identifying and trading with the prevailing trend in the market. Traders enter trades in the direction of the trend and aim to ride the trend until signs of reversal or exhaustion emerge.
- Mean Reversion: Mean reversion strategies capitalize on the tendency of prices to revert to their average or mean levels after extended periods of deviation. Traders look for overbought or oversold conditions and enter trades in anticipation of price reversals.
- Breakout Trading: Breakout strategies involve entering trades when the price breaks above resistance levels or below support levels. Traders aim to capture the momentum generated by the breakout and ride the trend in the direction of the breakout.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Swing Trading
To maximize success in swing trading, traders should avoid the following common mistakes:
- Ignoring Risk Management: Failing to implement proper risk management techniques can expose traders to significant losses, especially in volatile markets. Traders should always use stop-loss orders and position sizing to manage risk effectively.
- Overtrading: Overtrading occurs when traders take too many trades or trade with excessively large positions, leading to increased transaction costs and higher risk exposure. Traders should focus on quality setups and exercise patience in their trading.
- Chasing Price: Chasing price refers to entering trades at unfavorable prices after missing an initial move. This can lead to entering trades late and experiencing increased slippage and reduced profitability. Traders should wait for pullbacks or retracements before entering trades.
Resources and Further Reading for Successful Swing Trading
For traders looking to enhance their swing trading skills, there are numerous resources and books available:
- “Swing Trading for Dummies” by Omar Bassal
- “The Complete Swing Trading System” by Markus Heitkoetter
- “The Master Swing Trader” by Alan S. Farley
- Online courses and tutorials on swing trading strategies and techniques
- Financial websites and forums offering swing trading tips, analysis, and community support
Conclusion
Swing trading offers traders the opportunity to profit from short to medium-term price movements in financial markets. By adhering to key principles, utilizing technical analysis tools, identifying profitable setups, implementing effective entry and exit strategies, and managing risk appropriately, swing traders can enhance their chances of success and achieve consistent profitability. While swing trading requires patience, discipline, and continuous learning, mastering this trading style can lead to rewarding outcomes for traders seeking to capitalize on market trends and fluctuations.
Read our latest article on Forex Slippage
FAQs
- What is swing trading, and why are entry and exit strategies important in this approach?Answer: Swing trading involves capturing short- to medium-term price movements in financial markets. Entry and exit strategies are crucial because they determine the timing of trades, helping traders maximize profits and manage risk effectively.
- What is breakout trading, and how does it work in swing trading?Answer: Breakout trading involves entering trades when the price breaks above resistance levels or below support levels. This strategy anticipates the continuation of an existing trend or the start of a new trend, offering profitable trading opportunities.
- How do swing traders identify breakout trading opportunities?Answer: Swing traders identify breakout opportunities by looking for periods of consolidation or sideways movement in the price, followed by a decisive breakout accompanied by strong volume and momentum. Confirmation signals validate the breakout setup.
- What is pullback trading, and when is it used in swing trading?Answer: Pullback trading involves entering the market after a temporary retracement within the context of an existing trend. This strategy is employed when the price reverses against the trend before resuming its original direction, providing entry opportunities at more favorable prices.
- How do swing traders determine pullback trading setups?Answer: Swing traders identify pullback setups by recognizing established trends and key support or resistance levels where price retracements are likely to occur. Confirmation signals, such as reversal patterns, validate the end of the retracement and the resumption of the trend.
- What are trailing stop-loss orders, and how do swing traders use them?Answer: Trailing stop-loss orders are risk management tools that automatically adjust the stop-loss level as the price moves in the trader’s favor. Swing traders use trailing stops to protect profits and minimize losses while allowing for potential upside gains.
- How do swing traders set initial stop-loss levels for their trades?Answer: Swing traders set initial stop-loss levels based on factors such as their risk tolerance, account size, and the volatility of the asset being traded. The stop-loss is typically placed below (in an uptrend) or above (in a downtrend) key support or resistance levels.
- What role do confirmation signals play in entry and exit strategies for swing trading?Answer: Confirmation signals validate trade setups and provide entry and exit points for swing traders. These signals include price patterns, volume analysis, and other technical indicators that confirm the strength and direction of the trend.
- How do swing traders manage risk when implementing entry and exit strategies?Answer: Swing traders manage risk by setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on each trade. They also use position sizing techniques and risk-reward ratios to ensure that potential losses are smaller than potential gains.
- What are some common mistakes to avoid when using entry and exit strategies in swing trading?Answer: Common mistakes include ignoring confirmation signals, setting stop-loss levels too close to the entry price, and failing to adapt to changing market conditions. It’s essential for swing traders to stick to their trading plan and continuously evaluate and adjust their strategies for optimal performance.
Click here to read more on Swing Trading