Introduction
In the vast and dynamic world of forex trading, understanding currency pairs is fundamental. Currency pairs are the backbone of the forex market, representing the relative value of one currency compared to another. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting out, grasping the intricacies of currency pairs is crucial for success in the forex market.
What are Currency Pairs in Forex?
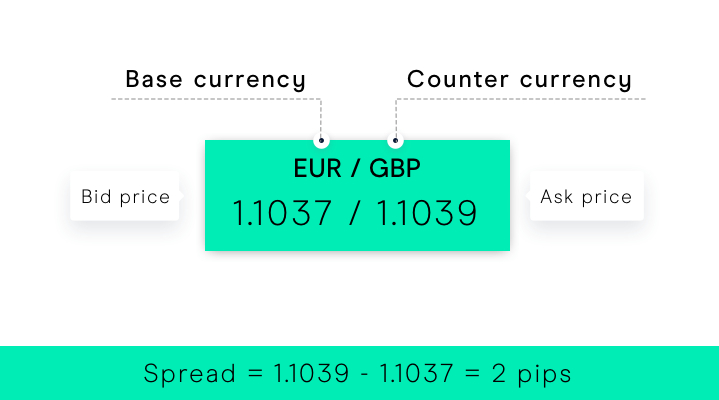
A currency pair is a quotation of two different currencies, where one currency is quoted against the other. For instance, in the pair EUR/USD, the euro (EUR) is the base currency, and the US dollar (USD) is the quote currency. This means that one unit of the base currency (EUR) is equivalent to a certain number of units of the quote currency (USD).
Top Forex Currency Pairs
Forex traders commonly deal with a variety of currency pairs, but some are more frequently traded than others. These are categorized into major, minor, and exotic currency pairs.
Major Currency Pairs and Minor Currency Pairs
Major Currency Pairs:
Major currency pairs are the backbone of the forex market, representing the most liquid and widely traded currencies worldwide. These pairs typically involve currencies from economically stable and developed countries, with the US dollar (USD) frequently serving as one of the currencies in the pair. The major currency pairs include:
- EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar): EUR/USD is the most traded currency pair in the forex market, representing the eurozone’s euro against the US dollar. It is highly liquid and renowned for its tight spreads, making it a favorite among traders of all levels.
- GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar): GBP/USD, also known as “Cable,” features the British pound sterling against the US dollar. It attracts significant trading volume and attention, particularly due to the economic importance of the United Kingdom and its close ties to the US economy.
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen): USD/JPY is a major currency pair representing the US dollar against the Japanese yen. It is heavily influenced by economic policies and monetary interventions from both the US Federal Reserve and the Bank of Japan.
- USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc): USD/CHF involves the US dollar and the Swiss franc, two currencies known for their stability and safe-haven status. This pair often reflects investor sentiment and geopolitical tensions, as Switzerland’s neutrality and financial prowess contribute to its appeal as a safe-haven currency.
Minor Currency Pairs (Cross-Currency Pairs):
Minor currency pairs, also referred to as cross-currency pairs, do not include the US dollar as one of the currencies in the pair. While they may not enjoy the same level of liquidity and trading volume as major pairs, they still offer ample trading opportunities for forex traders. Some examples of minor currency pairs include:
- EUR/GBP (Euro/British Pound): EUR/GBP represents the exchange rate between the euro and the British pound sterling. It is influenced by economic data releases from both the eurozone and the United Kingdom, as well as broader market sentiment regarding Brexit developments and Eurozone monetary policy.
- GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen): GBP/JPY pairs the British pound with the Japanese yen. This pair is known for its volatility, influenced by economic data from the UK and Japan, as well as risk sentiment in the global financial markets.
- AUD/CAD (Australian Dollar/Canadian Dollar): AUD/CAD reflects the exchange rate between the Australian dollar and the Canadian dollar. It is influenced by commodity prices, particularly crude oil and metals, as well as economic indicators from Australia and Canada.
While minor currency pairs may have slightly wider spreads and lower liquidity compared to major pairs, they still present opportunities for traders to diversify their portfolios and capitalize on specific currency movements. Understanding the dynamics of both major and minor currency pairs is essential for navigating the forex market effectively and executing successful trading strategies.
Exotic Currency Pairs
Exotic currency pairs represent a unique subset of the forex market, combining one major currency with a currency from a developing or emerging market. These pairs, such as USD/TRY (US dollar/Turkish lira) or EUR/TRY (Euro/Turkish lira), offer distinctive trading opportunities but also present specific challenges for forex traders. Here’s an in-depth look at exotic currency pairs:
- Characteristics of Exotic Currency Pairs: Exotic currency pairs typically exhibit several distinguishing characteristics:
- Wider Spreads: Exotic pairs often have wider bid-ask spreads compared to major and minor pairs. This wider spread can increase trading costs for traders.
- Lower Liquidity: Exotic pairs generally have lower trading volumes and liquidity compared to major and minor pairs. As a result, executing trades in exotic pairs may encounter slippage, where the execution price differs from the expected price.
- Higher Volatility: Exotic pairs tend to experience greater price fluctuations and volatility compared to major and minor pairs. This heightened volatility can present both opportunities and risks for traders.
- Unique Economic Factors: Exotic pairs are influenced by the economic conditions and geopolitical factors specific to the countries involved. Factors such as political instability, regulatory changes, or economic reforms in emerging markets can have a significant impact on exotic currency pairs.
- Trading Considerations for Exotic Currency Pairs: Trading exotic currency pairs requires careful consideration and risk management due to their unique characteristics:
- Risk Assessment: Traders should assess the risks associated with exotic pairs, including volatility, liquidity constraints, and potential geopolitical developments. Understanding the specific dynamics of the countries involved is crucial for effective risk management.
- Position Sizing: Given the higher volatility and wider spreads of exotic pairs, traders should adjust their position sizes accordingly to accommodate increased risk. Proper position sizing helps mitigate potential losses and preserves trading capital.
- Market Analysis: Conducting thorough fundamental and technical analysis is essential when trading exotic pairs. Traders should stay informed about economic indicators, central bank policies, and geopolitical events affecting the countries in the pair.
- Use of Limit Orders: Due to the wider spreads and lower liquidity of exotic pairs, traders may benefit from using limit orders to enter and exit positions at predetermined price levels. Limit orders help ensure execution at desired prices, reducing the impact of slippage.
- Diversification: While exotic pairs can offer unique trading opportunities, traders should diversify their portfolios across different currency pairs to spread risk effectively. Balancing exposure to exotic pairs with major and minor pairs can help mitigate overall portfolio risk.
- Long-Term Potential and Caution: While exotic currency pairs can offer the potential for significant profits due to their volatility, traders should approach them with caution. The higher risk associated with exotic pairs requires a disciplined and strategic approach to trading. Long-term success in trading exotic pairs hinges on thorough research, prudent risk management, and adaptability to changing market conditions.
In summary, exotic currency pairs present unique opportunities and challenges for forex traders. While they offer the potential for enhanced profitability, traders must carefully assess the risks involved and implement robust risk management strategies. With careful consideration and diligent analysis, traders can navigate the complexities of exotic pairs and capitalize on their trading potential in the dynamic forex market landscape.
Factors that Influence Currency Pair Movements
Understanding what drives currency pair movements is essential for successful trading. Several factors can impact exchange rates, including:
- Economic Indicators: Economic indicators serve as vital benchmarks for assessing the health and performance of economies, thus exerting significant influence on currency pair movements. Key economic indicators include:
- GDP Growth: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth rates indicate the pace of economic expansion or contraction in a country. Strong GDP growth often leads to currency appreciation, reflecting confidence in the economy.
- Employment Figures: Employment data, such as unemployment rates and non-farm payroll reports, provide insights into labor market conditions. Improvements in employment figures typically strengthen a currency, signaling economic growth and increased consumer spending.
- Inflation Rates: Inflation measures the rate at which prices for goods and services rise over time. Central banks closely monitor inflation rates and may adjust monetary policies, such as interest rates, to maintain price stability. Higher inflation rates can erode purchasing power and lead to currency depreciation.
- Central Bank Policies: Central banks implement monetary policies, including interest rate decisions and quantitative easing measures, to manage inflation, stimulate economic growth, and maintain financial stability. Changes in central bank policies can have profound impacts on currency values, as they influence investor perceptions of a country’s economic prospects.
- Geopolitical Events: Geopolitical events encompass political developments, conflicts, diplomatic relations, and trade tensions between countries, all of which can disrupt currency markets. Examples include:
- Political Instability: Political uncertainty and instability, such as government upheavals, elections, or regime changes, can lead to currency volatility and flight to safe-haven assets.
- Conflicts: Armed conflicts, geopolitical tensions, and international disputes can heighten risk aversion and trigger capital outflows from affected countries, leading to currency depreciation.
- Trade Tensions: Trade disputes, tariffs, and protectionist measures between countries can impact trade flows, supply chains, and economic growth prospects, influencing currency pair movements accordingly.
- Interest Rates: Central banks’ decisions on interest rates are among the most influential factors driving currency pair movements. Interest rate differentials between countries affect capital flows and exchange rates:
- Higher Interest Rates: Countries with higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investment, as investors seek higher returns on their capital. Consequently, currencies associated with higher interest rates typically appreciate against currencies with lower interest rates.
- Interest Rate Expectations: Anticipation of future interest rate changes, based on central bank statements, economic data, and market speculation, can lead to preemptive adjustments in currency pair valuations.
- Market Sentiment: Market sentiment reflects traders’ perceptions, emotions, and collective behavior, influencing short-term currency pair movements:
- Risk Appetite vs. Risk Aversion: Market sentiment oscillates between risk-on and risk-off environments, depending on factors such as economic data releases, geopolitical developments, and global events. Risk-on sentiment favors higher-yielding currencies and risk assets, while risk-off sentiment drives demand for safe-haven currencies like the US dollar, Japanese yen, and Swiss franc.
- News and Rumors: Market sentiment can shift rapidly in response to breaking news, rumors, and speculative reports. Traders closely monitor news outlets, social media platforms, and financial news websites for updates that may impact currency markets.
Understanding and analyzing these factors enable traders to make informed decisions, manage risks effectively, and capitalize on trading opportunities in the dynamic forex market environment. By staying abreast of economic developments, geopolitical events, interest rate movements, and market sentiment, traders can navigate currency pair movements with greater confidence and success.
What Affects the Rates of Currency Pairs
Several interrelated factors contribute to the rates of currency pairs:
- Supply and Demand: Like any other asset, currencies are subject to the laws of supply and demand. Increased demand for a currency will cause its value to appreciate, while excess supply will lead to depreciation.
- Trade Balances: A country’s trade balance, reflecting the difference between exports and imports, can impact its currency’s value. A trade surplus (exports > imports) usually strengthens the currency, while a trade deficit (imports > exports) may weaken it.
- Central Bank Interventions: Central banks may intervene in the forex market to stabilize or manipulate their currency’s value. Intervention strategies can include buying or selling currencies or adjusting interest rates.
- Speculation: Speculative trading activity by institutional investors, hedge funds, and individual traders can cause rapid fluctuations in currency pair rates, especially in highly liquid pairs.
Tips for Trading Forex Pairs
To navigate the forex market successfully, consider the following tips:
- Conduct Thorough Research: Staying informed about economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment is paramount in forex trading. Economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and employment figures provide insights into a country’s economic health, influencing its currency’s value.
- Geopolitical events like elections, trade agreements, or conflicts can cause sudden market movements, making it crucial to monitor global developments. Additionally, understanding market sentiment helps anticipate potential shifts in currency pair movements, allowing traders to adapt their strategies accordingly.
- Develop a Trading Strategy: Establishing a robust trading strategy is vital for consistent profitability in forex trading. This includes defining clear entry and exit points based on technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both. Incorporating risk management rules, such as setting stop-loss and take-profit orders, helps mitigate losses and protect profits. Position sizing strategies ensure that each trade aligns with risk tolerance and account size, preventing overexposure to market fluctuations.
- Practice Risk Management: Effective risk management is key to long-term success in forex trading. Utilizing stop-loss orders helps limit potential losses by automatically closing positions at predefined price levels. Limit orders allow traders to exit trades at specified profit targets, ensuring that winning trades are capitalized upon. Proper position sizing, based on risk-reward ratios and account equity, prevents excessive losses and preserves trading capital during adverse market conditions.
- Stay Disciplined: Discipline is the cornerstone of successful forex trading, as it enables traders to adhere to their trading plans consistently. Emotions like fear, greed, and impulsivity can cloud judgment and lead to impulsive decision-making, resulting in significant losses.
- By sticking to predefined trading rules and avoiding emotional reactions to market fluctuations, traders maintain focus and consistency in their trading approach. Patience and discipline are essential virtues that separate successful traders from those who succumb to emotional impulses.
- Continuously Learn: The forex market is dynamic and ever-evolving, requiring traders to adapt and stay informed about emerging trends, strategies, and technological advancements. Engaging in ongoing education through seminars, webinars, online courses, and reputable trading forums enhances trading skills and expands market knowledge.
- Keeping abreast of innovative tools, such as algorithmic trading platforms and advanced charting software, empowers traders to optimize their trading strategies and capitalize on market opportunities more efficiently. Continuous learning fosters growth, adaptability, and resilience in the face of evolving market conditions.
By incorporating these expanded tips into their trading routines, forex traders can enhance their decision-making processes, manage risks effectively, and strive for long-term success in the dynamic and challenging forex market landscape.
Conclusion
Currency pairs are the cornerstone of forex trading, representing the relative value of different currencies in the global market. Understanding the dynamics of currency pairs, including major, minor, and exotic pairs, as well as the factors influencing their movements, is essential for successful trading. By staying informed, developing robust trading strategies, and practicing disciplined risk management, traders can navigate the complexities of the forex market and seize profitable opportunities.
Read our latest article on Forex Spread Trading
FAQs
1. What are currency pairs in Forex trading?
- Currency pairs in Forex trading represent the relative value of one currency compared to another. They consist of two currencies, where one is quoted against the other, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY.
2. What distinguishes major currency pairs from minor currency pairs?
- Major currency pairs involve the most heavily traded currencies globally, such as EUR/USD and USD/JPY, while minor currency pairs do not include the US dollar, such as EUR/GBP and GBP/JPY.
3. What are exotic currency pairs, and how do they differ from major and minor pairs?
- Exotic currency pairs involve one major currency and one currency from a developing or emerging market, such as USD/TRY or EUR/TRY. They typically have wider spreads, lower liquidity, and higher volatility compared to major and minor pairs.
4. What factors influence currency pair movements in Forex trading?
- Currency pair movements in Forex trading are influenced by various factors, including economic indicators, geopolitical events, interest rates, and market sentiment.
5. How do economic indicators impact currency pair movements?
- Economic indicators such as GDP growth, employment figures, inflation rates, and central bank policies can significantly influence currency values by providing insights into a country’s economic health and performance.
6. What role do geopolitical events play in currency pair movements?
- Geopolitical events such as political instability, conflicts, elections, and trade tensions between countries can cause fluctuations in currency pairs by affecting investor sentiment and risk perceptions.
7. How do interest rate decisions affect currency pair movements?
- Central banks’ decisions on interest rates influence currency values, with higher interest rates attracting foreign investment and strengthening the currency, while lower interest rates may lead to currency depreciation.
8. How does market sentiment impact currency pair movements?
- Market sentiment, driven by trader perceptions and psychology, plays a crucial role in determining currency pair movements. Sentiment can shift rapidly based on news, rumors, and market speculation, influencing trading decisions.
9. What are some tips for trading currency pairs effectively?
- Tips for trading currency pairs include conducting thorough research, developing a trading strategy with clear entry and exit points, practicing risk management with stop-loss and limit orders, staying disciplined, and continuously learning about market trends and strategies.
10. Why is it essential to understand and analyze factors influencing currency pair movements in Forex trading?
- Understanding and analyzing factors influencing currency pair movements enable traders to make informed decisions, manage risks effectively, and capitalize on trading opportunities in the dynamic Forex market environment, ultimately contributing to trading success and profitability.
Click here to read more on Currency Pairs