In the dynamic world of forex trading, investors are often exposed to various risks stemming from volatile currency fluctuations. To mitigate these risks and safeguard investments, traders employ a strategy known as hedging. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the concept of forex hedging, its benefits, different strategies, implementation techniques, associated risks, best practices, and real-world examples.
Understanding the Concept of Hedge in Forex Trading
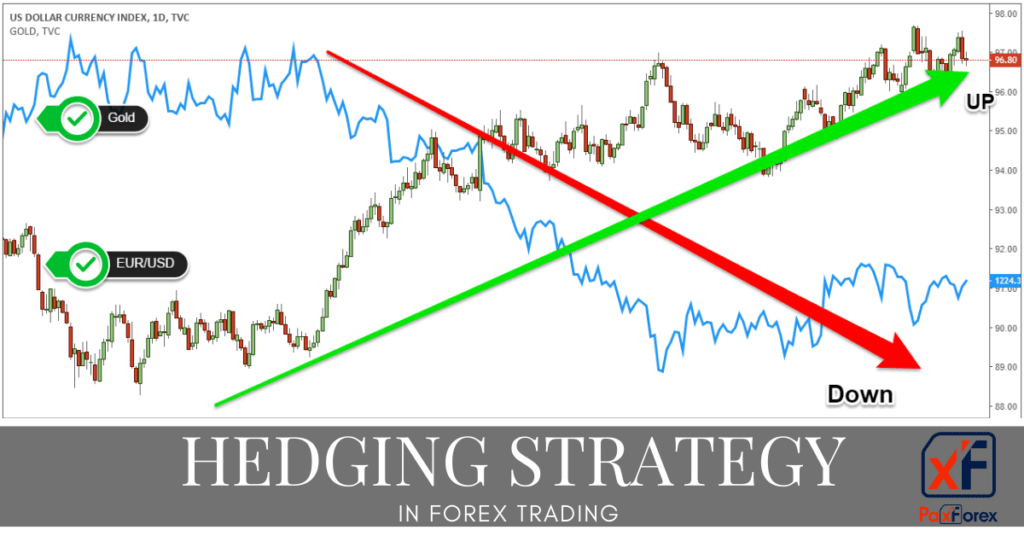
Hedging in forex trading involves strategically offsetting or mitigating the risks associated with currency fluctuations. It is a proactive approach aimed at protecting investments from adverse market movements. Hedging allows traders to establish positions that act as insurance against potential losses in existing positions, thereby minimizing overall risk exposure.
Benefits of Forex Hedging
Forex hedging offers several key benefits to traders:
- Risk Mitigation: Forex hedging serves as a powerful tool for mitigating risk in the volatile currency markets. By employing hedging strategies, traders can effectively reduce their exposure to adverse currency movements, thereby minimizing the potential impact of market volatility on their investments. Hedging acts as a form of insurance, providing a buffer against unexpected fluctuations in exchange rates and helping traders preserve capital during turbulent market conditions.
- Protection of Profits: One of the primary benefits of forex hedging is its ability to protect profits from existing positions. In situations where traders have accumulated profits from successful trades, hedging allows them to lock in those gains and protect against potential losses in the event of adverse market movements. By hedging profitable positions, traders can secure their earnings and safeguard against market reversals, ensuring that their hard-earned profits are preserved even in the face of unfavorable market conditions.
- Enhanced Stability: Hedging strategies contribute to the overall stability of investment portfolios, particularly in times of uncertainty or market turbulence. By hedging against potential risks and losses, traders can create a more resilient portfolio that is better equipped to withstand market fluctuations. This enhanced stability provides traders with greater peace of mind and confidence in their investment decisions, enabling them to navigate through uncertain market environments with a sense of security and assurance.
- Increased Flexibility: Forex hedging offers traders increased flexibility in managing their risk exposure and adjusting to changing market conditions. Hedging allows traders to tailor their portfolio positions according to their risk tolerance, investment objectives, and market outlook. Whether it involves hedging specific currency pairs, adjusting position sizes, or incorporating different hedging instruments, traders can adapt their hedging strategies to meet evolving market dynamics. This flexibility enhances portfolio management capabilities, allowing traders to optimize risk-reward ratios and capitalize on opportunities while minimizing potential downside risks.
Different Types of Forex Hedging Strategies
There are various hedging strategies employed in forex trading, each serving specific purposes and catering to different risk profiles. Some common types of forex hedging strategies include:
- Direct Hedging: Direct hedging is a straightforward strategy that involves opening a position in the opposite direction to an existing trade to offset potential losses. For example, if a trader holds a long position (buy) on a currency pair, they may open a short position (sell) on the same currency pair of equal size. This effectively hedges the trader’s exposure to fluctuations in the exchange rate, as gains in one position can offset losses in the other. Direct hedging is commonly used to protect against short-term market fluctuations while maintaining the original trading position.
- Multiple Currency Pairs Hedging: Multiple currency pairs hedging utilizes correlated currency pairs to hedge against exposure in one currency by taking offsetting positions in another. Traders identify currency pairs that have a strong correlation and enter into positions that offset each other’s risk. For example, if a trader holds a long position on EUR/USD, they may simultaneously open a short position on GBP/USD, as these two currency pairs often move in tandem. By hedging across multiple currency pairs, traders can diversify their risk and reduce overall exposure to currency fluctuations.
- Options Hedging: Options hedging involves using currency options contracts to protect against adverse currency movements while retaining the flexibility to benefit from favorable movements. Traders can purchase options contracts that give them the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency pair at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specified timeframe (expiry date). By purchasing options contracts, traders can protect against downside risk while allowing for unlimited upside potential. Options hedging provides traders with insurance against adverse market movements while still allowing them to capitalize on favorable price movements.
- Forward Contracts: Forward contracts entail entering into agreements to exchange currencies at predetermined rates in the future, providing protection against exchange rate fluctuations. In a forward contract, two parties agree to buy or sell a specified amount of currency at an agreed-upon exchange rate at a future date. Forward contracts are commonly used by businesses and investors to hedge against currency risk arising from international trade or investments. By locking in exchange rates in advance, traders can protect themselves against adverse currency movements and eliminate uncertainty regarding future exchange rate fluctuations.
Each of these forex hedging strategies offers unique advantages and considerations, catering to different risk profiles and investment objectives. Traders should carefully assess their risk exposure and market outlook to determine the most suitable hedging strategy for their specific needs. Additionally, it’s essential to consider factors such as transaction costs, liquidity, and regulatory considerations when implementing hedging strategies in forex trading.
Implementing a Forex Hedging Strategy
Implementing a forex hedging strategy requires careful planning and execution. Traders must assess their risk exposure, identify suitable hedging instruments, and execute trades in a timely manner. Key steps in implementing a forex hedging strategy include:
1. Assessing Risk Exposure: Before implementing a forex hedging strategy, traders must conduct a comprehensive assessment of their risk exposure. This involves identifying the currency risks inherent in existing positions, including potential losses resulting from adverse currency movements. Traders should analyze factors such as the size of their positions, the currency pairs involved, and the duration of their trades. By understanding their risk exposure, traders can determine the appropriate hedging approach that aligns with their risk tolerance and investment objectives.
2. Selecting Hedging Instruments: Once traders have assessed their risk exposure, they need to select suitable hedging instruments to mitigate potential losses. The choice of hedging instruments depends on various factors, including the trader’s risk profile, market outlook, and hedging objectives. Common hedging instruments include forward contracts, options, and derivatives. Traders should evaluate the features and characteristics of each instrument, such as cost, liquidity, and flexibility, to determine which best meets their hedging needs.
3. Executing Trades: After selecting the appropriate hedging instruments, traders must execute trades in a timely and efficient manner. This involves entering into hedging positions at optimal entry points to effectively offset potential losses in existing positions. Traders should consider factors such as market liquidity, pricing dynamics, and transaction costs when executing hedging trades. It’s essential to closely monitor market conditions and seize opportunities to enter hedging positions at favorable levels to maximize effectiveness.
4. Monitoring and Adjusting: Implementing a forex hedging strategy is not a one-time event but an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. Traders should regularly monitor market conditions and assess the performance of their hedging positions. If market dynamics change or new information becomes available, traders may need to adjust their hedging positions accordingly to maintain alignment with their investment objectives and risk management goals. By staying vigilant and proactive, traders can adapt their hedging strategies to evolving market conditions and optimize their risk-adjusted returns.
In summary, implementing a forex hedging strategy involves careful planning, assessment of risk exposure, selection of suitable hedging instruments, timely execution of trades, and continuous monitoring and adjustment. By following these key steps and remaining disciplined in their approach, traders can effectively mitigate risk and safeguard their investments in the dynamic currency markets.
Risks and Challenges of Forex Hedging
While forex hedging offers significant benefits, it also comes with certain risks and challenges that traders must be aware of:
1. Cost Considerations: One of the primary risks associated with forex hedging is the impact of transaction costs on overall profitability. Hedging transactions may incur additional costs, such as brokerage fees, spreads, and premiums for options contracts. These costs can eat into profits and diminish the effectiveness of hedging strategies. Traders should carefully consider the cost implications of hedging and ensure that the potential benefits outweigh the associated expenses.
2. Execution Risk: Poorly timed or executed hedging trades pose a significant risk to traders. If hedging positions are entered into at the wrong time or executed incorrectly, they may fail to effectively offset losses in existing positions. This can result in increased risk exposure and potential losses for traders. To mitigate execution risk, traders should conduct thorough analysis, use appropriate risk management techniques, and execute trades with precision and discipline.
3. Over-Hedging: Another challenge associated with forex hedging is the risk of over-hedging. Excessive hedging can lead to a situation where traders limit their potential upside gains while simultaneously reducing overall portfolio performance, especially in trending markets. Over-hedging may occur when traders employ multiple hedging strategies simultaneously or hedge excessively against minor fluctuations in currency prices. Traders should carefully assess their hedging needs and avoid over-hedging to maintain a balanced risk-reward profile.
4. Market Risk: Despite their intended purpose, hedging strategies are not immune to market risks. Unexpected market developments, such as geopolitical events, economic data releases, or sharp movements in currency prices, can undermine the effectiveness of hedging positions. Market risk can result in losses for traders, even if they have implemented hedging strategies to protect against adverse currency movements. To manage market risk, traders should stay informed about market dynamics, continuously monitor market conditions, and remain flexible in their hedging approach to adapt to changing circumstances.
In summary, while forex hedging offers significant benefits in terms of risk mitigation and portfolio protection, traders must be aware of the potential risks and challenges involved. By carefully considering cost implications, mitigating execution risk, avoiding over-hedging, and managing market risk effectively, traders can maximize the effectiveness of their hedging strategies and protect their investments in the dynamic currency markets.
Best Practices for Successful Forex Hedging
1. Understand the Purpose: Before implementing any hedging strategy, it’s essential to clearly define the objectives and purpose behind it. Traders should identify the specific risks they seek to hedge against and ensure that the hedging strategy aligns with their overall investment goals and risk management principles. Whether the objective is to protect profits, minimize downside risk, or manage exposure to currency fluctuations, a clear understanding of the purpose is crucial for effective hedging.
2. Diversify Hedging Instruments: Utilizing a combination of hedging instruments can enhance the effectiveness of hedging strategies and mitigate risks associated with relying on a single approach. Traders should consider diversifying their hedging instruments across different asset classes, such as options, forwards, and derivatives, to optimize hedging effectiveness across various market conditions. Diversification helps spread risk and provides greater flexibility in managing portfolio exposure, allowing traders to adapt to changing market dynamics more effectively.
3. Regular Review and Adjustment: Successful forex hedging requires continuous monitoring and adjustment of hedging positions to ensure alignment with risk management objectives and changing market conditions. Traders should regularly review their hedging positions, assess their performance, and make necessary adjustments as needed. This may involve rebalancing hedge ratios, rolling forward contracts, or closing out ineffective positions. By staying vigilant and proactive, traders can maintain optimal hedging effectiveness and respond promptly to evolving market dynamics.
4. Maintain Flexibility: Flexibility is essential in forex hedging strategies to capitalize on emerging opportunities while effectively managing downside risks. Traders should remain adaptable and open to adjusting their hedging strategies in response to changing market conditions, economic developments, or shifts in risk appetite. This may involve modifying hedging ratios, exploring new hedging instruments, or implementing dynamic hedging approaches. By maintaining flexibility, traders can optimize risk-adjusted returns and navigate through volatile market environments with confidence.
In summary, adhering to these best practices can help traders maximize the effectiveness of their forex hedging strategies and achieve their risk management objectives. By understanding the purpose of hedging, diversifying hedging instruments, regularly reviewing and adjusting positions, and maintaining flexibility, traders can enhance their ability to protect investments and navigate through uncertain market conditions successfully.
Tools and Resources for Forex Hedging
Various tools and resources are available to assist traders in implementing effective forex hedging strategies:
- Trading Platforms: Choose a reliable trading platform that offers access to a wide range of hedging instruments and analytical tools to facilitate effective hedging execution.
- Economic Calendars: Stay informed about key economic events and announcements that may impact currency markets, enabling timely adjustments to hedging positions.
- Risk Management Tools: Utilize risk management tools such as stop-loss orders, limit orders, and trailing stops to manage risk exposure and protect investments.
- Education and Training: Invest in ongoing education and training to stay updated on hedging techniques, market trends, and best practices in forex trading.
Case Studies: Successful Forex Hedging Examples
Real-world examples of successful forex hedging can provide valuable insights into effective hedging strategies and their impact on investment outcomes. Case studies highlighting instances where hedging strategies have effectively protected investments or enhanced portfolio performance offer practical lessons for traders.
. Case Study: XYZ Corporation
XYZ Corporation, a multinational company, operates in various countries and is exposed to currency risk due to its international operations. To mitigate this risk, XYZ implements a forward contract hedging strategy to protect its revenue and profits from adverse currency movements.
In this example, XYZ has significant receivables denominated in euros, which it expects to receive in six months. Concerned about potential depreciation of the euro against its domestic currency, XYZ enters into a six-month forward contract to sell euros and buy its domestic currency at a predetermined exchange rate.
As a result of this forward contract, XYZ effectively locks in the exchange rate, ensuring that it will receive the agreed-upon amount of domestic currency regardless of future currency fluctuations. If the euro depreciates as anticipated, XYZ will benefit from the favorable exchange rate, offsetting any losses in its euro-denominated receivables.
This successful hedging strategy allows XYZ Corporation to protect its revenue and profits from currency volatility, providing stability and predictability to its financial performance.
2. Case Study: Individual Forex Trader
An individual forex trader, John, specializes in trading major currency pairs and is exposed to currency risk in his trading portfolio. To manage this risk, John implements a options hedging strategy using currency options contracts.
In this scenario, John holds a long position in EUR/USD, anticipating a bullish movement in the euro against the US dollar. However, he is concerned about potential downside risks if the euro depreciates unexpectedly. To protect his position, John purchases put options on EUR/USD, giving him the right to sell euros at a predetermined exchange rate within a specified timeframe.
If the euro depreciates as John feared, the put options will increase in value, providing him with a hedge against potential losses in his long position. Conversely, if the euro appreciates, John can allow the options contracts to expire worthless, limiting his loss to the premium paid for the options.
This options hedging strategy allows John to protect his trading capital and manage risk effectively, enabling him to capitalize on favorable market movements while safeguarding against adverse outcomes.
These case studies illustrate how successful forex hedging strategies can effectively protect investments and enhance portfolio performance in real-world scenarios. By implementing appropriate hedging techniques tailored to their specific needs and objectives, traders and corporations alike can mitigate currency risk and achieve greater stability and predictability in their financial operations.
Conclusion: The Importance of Forex Hedging in Safeguarding Investments
In conclusion, forex hedging plays a vital role in protecting investments and managing risk in the currency markets. By understanding the concept of hedging, implementing appropriate strategies, and adhering to best practices, traders can mitigate the impact of adverse currency movements and enhance portfolio stability. Through careful planning, execution, and continuous monitoring, forex hedging empowers traders to navigate through volatile market conditions with confidence and safeguard their investments effectively.
Read our latest article on Trading Loss
FAQs
- What is forex hedging, and why is it important?
- Forex hedging involves strategies used by traders to mitigate risks associated with currency fluctuations. It’s essential because it helps protect investments from potential losses due to adverse market movements.
- What are the benefits of forex hedging?
- Forex hedging offers benefits such as risk mitigation, protection of profits, enhanced portfolio stability, and increased flexibility in managing risk exposure.
- What are some common types of forex hedging strategies?
- Common types of forex hedging strategies include direct hedging, multiple currency pairs hedging, options hedging, and forward contracts.
- How can traders implement a forex hedging strategy effectively?
- Traders can implement a forex hedging strategy effectively by assessing their risk exposure, selecting suitable hedging instruments, executing trades in a timely manner, and continuously monitoring and adjusting positions.
- What are the risks and challenges associated with forex hedging?
- Risks and challenges of forex hedging include cost considerations, execution risk, over-hedging, and market risk, which traders must be aware of and manage effectively.
- What are some best practices for successful forex hedging?
- Best practices for successful forex hedging include understanding the purpose of the hedge, diversifying hedging instruments, regularly reviewing and adjusting positions, and maintaining flexibility in hedging strategies.
- How can real-world case studies help traders understand forex hedging better?
- Real-world case studies provide practical examples of successful forex hedging strategies in action, offering valuable insights and lessons for traders to learn from.
- What are some key considerations when selecting hedging instruments?
- Key considerations when selecting hedging instruments include cost, liquidity, flexibility, and alignment with risk management objectives and investment goals.
- How can traders assess their risk exposure in forex trading?
- Traders can assess their risk exposure by analyzing factors such as position sizes, currency pairs involved, market volatility, and potential impact of currency fluctuations on their investments.
- Why is it important to maintain flexibility in forex hedging strategies?
- Maintaining flexibility in forex hedging strategies allows traders to adapt to changing market conditions, capitalize on emerging opportunities, and manage downside risks effectively, enhancing overall portfolio performance.
Click here to read more on Forex Hedging